FIFO Method Explanation And Illustrative Examples
If the store already carries the product, this scan updates the quantity already in stock. When a customer buys one of these products, the database lists one less product in its count. At any time, the store manager can review the database to learn how much of that product is currently in stock and whether they need to order more. Other businesses that need perpetual inventory include those that specialize in drop shipping, where the manufacturers ship directly to customers or those who specialize in trade and distribution. Understanding which stock is available at a given time requires constant updates or a perpetual system. Under the FIFO method, it’s assumed that the oldest inventory items are sold first.
Perpetual vs. Periodic Inventory Systems
- Physical counts to reconcile the database are rare, but necessary, since the true inventory count can become skewed over time with theft, loss or breakage.
- As shown below in the ledger, estimate the relative percentages of both COGS and gross profit for your total sales.
- Practicing ethicalshort-term decision making may have prevented both scenarios.
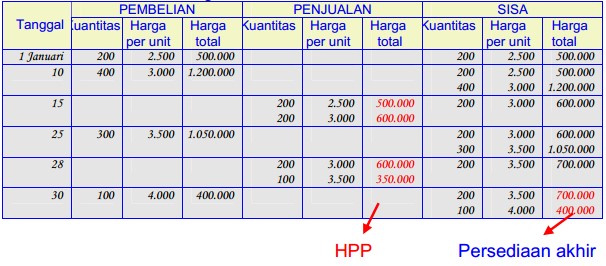
- To calculate ending Inventory cost using the FIFO Perpetual method can take a lot of work, and may require us to create a running tabular balance to keep track of how much we paid for each item.
Ending inventory was made up of 30 units at $21 each, 45units at $27 each, and 210 units at $33 each, for a total LIFOperpetual ending inventory value of $8,775. Once those units were sold,there remained 30 more units of beginning inventory. At the time of the secondsale of 180 units, the FIFO assumption directs the company to costout the last 30 units of the beginning inventory, plus 150 of theunits that had been purchased for $27. Thus, after two sales, thereremained 75 units of inventory that had cost the company $27 each.The last transaction was an additional purchase of 210 units for$33 per unit.
Cost Data for Calculations
The second way could be to adjust purchases and sales of inventory in the inventory ledger itself. The problem with this method is the need to measure value of sales every time a sale takes place (e.g. using FIFO, LIFO or AVCO methods). If accounting for sales and purchase is kept separate from accounting for inventory, the measurement of inventory need only be calculated once at the period end. This is a more practical and efficient approach to the accounting for inventory which is why it is the most common approach adopted.
Perpetual FIFO
So, the company’s management is responsible for determining the best cost flow assumption. The assumption is certainly a subjective matter, and the definition of “best” will depend on the business type. The preceding illustrations were based on the periodic inventory system. In other words, the ending inventory was counted and costs were assigned only at the end of the period. With a perpetual system, a running count of goods on hand is maintained at all times.
It is for this reason that the adoption of LIFO Method is not allowed under IAS 2 Inventories. If you need help with other Managerial Accounting Topics check out our archive or check out our list if you Need help with your accounting classes through the links to see our other offerings. If we take 100 units out of inventory, we would take them from beginning inventory. Our example has a four-day period, but we can use the same steps to calculate the ending inventory for a period of any duration, such as weeks, months, quarters, or years. Under the FIFO Method, inventory acquired by the earliest purchase made by the business is assumed to be issued first to its customers. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
Perpetual Inventory Systems
It has grown since the 1970s alongside the developmentof affordable personal computers. These UPC codes identify specific products butare not specific to the particular batch of goods that wereproduced. Thismore specific information allows better control, greateraccountability, increased efficiency, and overall qualitymonitoring of goods in inventory. 8615 instructions The technology advancements thatare available for perpetual inventory systems make it nearlyimpossible for businesses to choose periodic inventory and foregothe competitive advantages that the technology offers. The specific identification method of cost allocation directlytracks each of the units purchased and costs them out as they aresold.
Its supply chain provides deliveries daily of additional goods that the employees then scan into their database. If the product is new, the employee must add the details of the product when they initially scan it. That additional information includes a description, the product code or SKU and where customers will find it in the store.
LIFO (last-in, first-out) is a cost flow assumption that businesses use to value their stock where the last items placed in inventory are the first items sold. So the remaining inventory at the end of the period is the oldest purchased or produced. In a perpetual LIFO system, the last costs available at the time of the sale are the first that software moves from the inventory account and debits from the COGS account.

